Confused about all the abbreviations related to your air conditioning system?
EER and SEER sound the same but are pretty different. You must know the difference between them, especially as one is used as the standard for central AC systems, and the other is used only for portable AC!
Let’s take a little look at the main differences right now…

EER vs SEER
EER and SEER may sound similar but they are very different. Both of them measure the efficiency of an air conditioner by using the British Thermal Unit (BTU) figure to determine the ratio of cooling, and the wattage (W) a unit needs to do this.
EER is most commonly used in cooler climates. It is typically the rating given for portable air conditioners and window units. It is calculated based on a temperature of 95 °F.
SEER is used in warmer climates and is the standard rating for central air conditioning units all over the States. It is calculated based on a median from a range of temperatures, usually 85 °F.
What is an EER Rating?
EER or Energy Efficiency Ratio is a rating given to the efficiency of an item when it is at peak load capacity. The rating is standardized so that the consumer can compare different models with ease.
EER is used for all items that use energy, but in this case, we are referring to air conditioners in particular. The EER rating measures the efficiency of the air conditioner when it is operating at 95 °F.
Because this temperature is high, you can use the EER rating for an air conditioner to account for the item running constantly in a steady-state, whether on a warm or cool day.
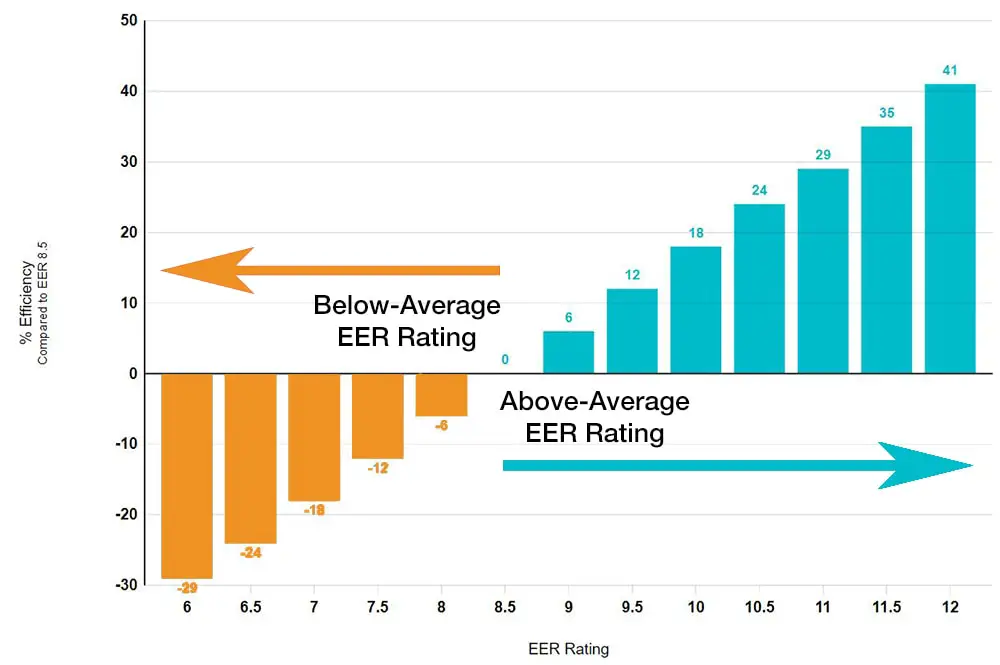
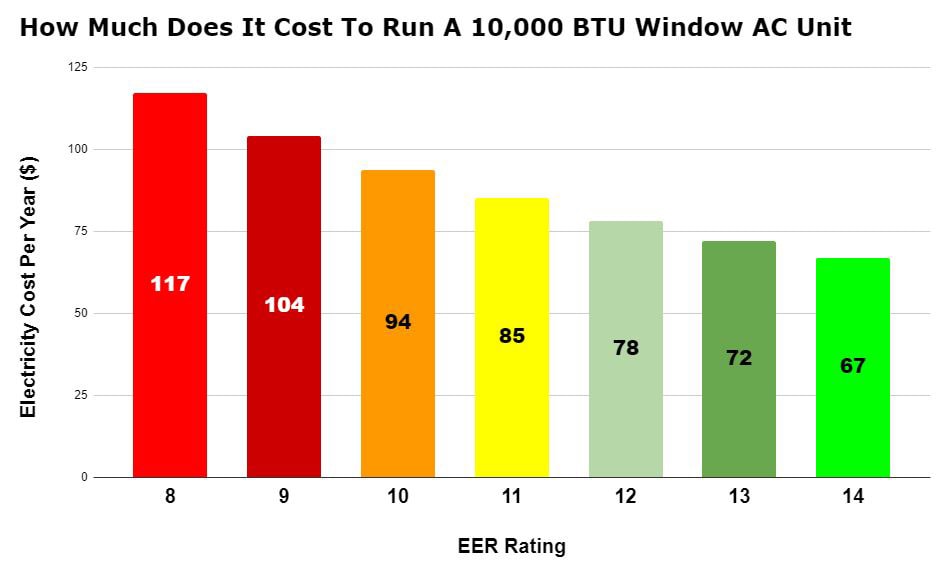
The higher your EER rating is, the more efficient the product is going to be, costing you less in the long run.
EER is an essential rating in all homes looking to reduce their environmental impact as it gives homeowners (or business owners) a quantifiable figure to aim for when trying to make their premises more environmentally friendly.
Something to bear in mind is that for an air conditioner, the EER accounts for just 2% of the operating hours of a unit for a typical, run-of-the-mill comfort cooling program, giving you a misleading figure overall.
How Do You Calculate EER?
Calculating an EER rating can be done with a simple equation. The figures that you need to complete the equation are the ratio of cooling energy (BTU) and the wattage needed to power the product. BTU is divided by the wattage (W).
The BTU measurement or British Thermal Units is representative of the energy needed to increase the temperature of a pound (lb) of water by 1 °F. Let’s see an example.
For an air conditioner that has 10,000 BTU and needs 1,200 W to power it, the equation would look like this:
10,000 BTU 1,200 W = 8.3
Remember that 8.3 refers to the EER rating so you must write it as 8.3 EER.
What is a SEER Rating?
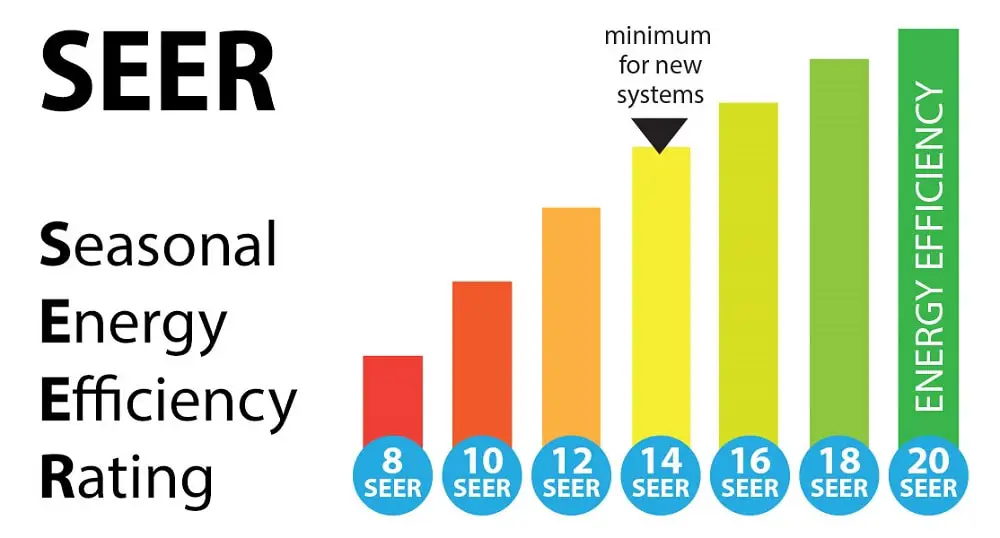
It may be just one letter, but SEER is very different from EER. SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio.
Like EER, it is a ratio worked out based on the cooling energy and output energy, but rather than taking into account year-round usage it assesses it based on seasonal use. It measures the efficiency of an air conditioner over a whole season.
This means it is most commonly used in climates where each season faces drastically different conditions and so year-round air conditioning is not needed. It is more common to see a SEER rating on central air conditioning, as opposed to portable or window units.
You should aim for your SEER rating to be as high as possible as this will mean that it is going to be the most efficient in terms of energy consumption. Choosing a higher rating could also cut down your yearly energy costs.
The SEER rating uses a variable temperature between 65 and 104 °F rather than the 95 °F of the EER. This checks its efficiency based on the variable temperature.
How Do You Calculate SEER?
Calculating SEER is not as straightforward as calculating EER. It is best to see it broken down into steps:
- Find out the British Thermal Units (BTU) per hour of your air conditioning unit.
- Find out the watts (W) used per hour for your unit.
- Calculate the BTU used per hour in the summer months (or whatever season you use the unit). This is usually around 1000 hours.
- Using the figure from step 2, multiply it by 1000 to find out the watts-hours used in the time period (i.e. the summer months).
- Using the figure from step 3 (the BTU used in summer months), take that and divide it by the watts-hours consumed in the same time from step 4. This will give you the SEER rating.
SEER to EER Converter
You can also use our SEER to EER converter below. Just input your SEER level and the corresponding EER level will be produced. Please note that this is just an estimation and not 100% accurate.
Relevant Characteristics Between EER and SEER
EER vs SEER
Compare by tapping or clicking below!
Option
EER
SEER
Rating Range
EER
A-G (1-100)
SEER
14-21 SEERs
Factors in Calculating
EER
British Thermal Units (BTU), Watts (W) and temperature (95℉)
SEER
British Thermal Units (BTU), Watts (W) and temperature (85℉)
Appliance Types
EER
Portable and Window Air Conditioners. Although, EER ratings are given to most appliances that are used in the home such as dryers, refrigerators, and other appliances.
SEER
Central Air Conditioning
Similarities and Differences
EER and SEER are both similar but have some differences, too. In this section, we are going to be exploring the similarities and differences of them alongside each other so you can compare and contrast.
EER and SEER Differences
Appliances
As you can see from the table above and from what we have already discussed about them, one of the main differences between EER and SEER is that EER is used for portable air conditioners and window units, whereas SEER is used for central air conditioning units.
SEER is used right across the United States as the default rating system for Central Air Conditioning systems. This is because it gives an average seasonal temperature that lies between a wider range (85 °F).
It is also worked out based on part-time usage. By this, we mean that it is worked out based on it being used for just 1000 hours in the summer months when it is most needed.
In comparison, EER is based on one temperature (95 °F) and is based on constant use.
Rating Range
Another difference between EER and SEER is that of the rating range.
SEERs rating range has changed through the years and will change again in 2023. It began starting at 8, then moving to 13, and then finally to 14 in 2015. What we mean by this is that the lowest SEER rating an appliance can have is 14. The range is between 14 and 21 for SEER.

EER uses letters from A-G to differentiate between ratings. A rating of ‘A’ means that an appliance is very efficient. ‘G’ is the lowest allowable efficiency rating. Within these letter-ratings are number ranges. 92-100 falls in ‘A’, so it is the highest. 1-20 is in ‘G’, the lowest.
Calculation
EER is a far simpler equation to work out compared with SEER that has many more steps.
Oftentimes, SEER has to be worked out on a computer if the product is being sold to consumers to ensure the most accurate calculation.
EER can be done even without a calculator.
EER and SEER Similarities
Factors in Calculating
The main similarity between EER and SEER is that both of them use the same factors for their calculations. Each of them takes into account the BTU of the appliance, the wattage needed to power it, and a measure of temperature to get an average.
Of course, as we know, the SEER calculation does require extra steps to work out very specific BTU and wattage based on the time of year, but they still use the same units of measure to do so.
Air conditioning
Whilst they may be used for different types of air conditioning, the fact remains that they are both closely linked to air conditioners. So much so that sometimes people (incorrectly) use the two abbreviations interchangeably.

What About IEER and COP Ratings?
IEER and COP are alternatives to EER and SEER. First, we need to explore them separately.
IEER
IEER is a recent development that addresses the efficiency of air conditioning equipment that operates at different loads. The IEER accounts for full and part loads by weighting EER figures at different loads and adding them together. It is based on the number (as an approximate) of hours a unit spends at each load.
COP
COP is yet another abbreviation that stands for Coefficient of Performance. It is used to tell us how effective an air conditioner (or heat pump) is at transferring heat. That is then compared to the amount of electrical power it uses to do this.
COP is not a standard requirement for air conditioners and HVAC equipment, but it does have a set standard for heat pumps.
Similarities and Differences
There are certainly similarities and differences between IEER and COP, especially in relation to EER and SEER.

IEER is most commonly used for evaluating split system air conditioners. These are units that utilize several air handlers and may work in different conditions. This is in comparison to EER and SEER which only deals with one system.
COP is not required, unlike the other three abbreviations. It also uses no units to calculate it. What it does is measure instantaneous performance without factoring in time.
Why people see COP and IEER as potential alternatives
COP could be seen as a potential alternative because it involves just one simple figure. This means it is easy to calculate from published material and so it takes less time and is more straightforward.
IEER is seen as an alternative option because it deals with split systems which would, of course, be preferable to homes and businesses with a split AC system.
Tips to Maximize Your Air Conditioner’s Energy Efficiency
- When using your AC you should close all doors and windows to conserve the conditioned air. Air can easily escape through entrances. This will also stop more hot air from outside coming into your home. Also, you should seal up gaps and fix leaks around doors and windows.
- Ensure you change your AC filter often to rid it of any grime, dust, and other build-ups that could impact its efficiency. As well as this you can clean and vacuum the vents to ensure that they are rid of any debris that could cause inefficiencies. Consider a professional duct and vent clean, especially if you have pets that shed their fur.
- Schedule regular maintenance with a professional to prevent any issues from happening. Whilst you can keep on top of filter and vent cleaning, you need a professional to regularly do a deep clean and check for issues.
- You should increase the temperature on your thermostat by just 8 °F. You will still be cool enough but will save more energy. If 8 °F feels like too much of an increase just do a 5 °F increase, to begin with, and see how that feels.
- If your outside condenser is in the sun in any way you should consider shading it. This is because the heat of the sun can make the air conditioning system less efficient as the condensed air will be too hot. Use a fence, condenser cover, or any other structure that would give it suitable shade.
- If you have any appliances that create heat such as clothes dryers, ovens, or anything else that gives off warmth then keep them away from the thermostat, any vents, and limit your usage. Likewise, reduce the time spent in the kitchen using the oven, the grill, and the stove.

Bottom Line
There you have it, a guide on EER and SEER. we are sure that you can agree that whilst they may sound the same, they are both very different. Both EER and SEER are useful, and indeed, essential when it comes to air conditioning systems.
If you have a central air conditioning system then you will likely need to take note of the SEER rating. For portable air conditioning and window units then you should use EER as your rating.
Remember, the higher the rating of both EER and SEER, the more energy-efficient the unit will be, saving you money and conversing energy!
People Also Ask
Whilst we have tried to answer any query you might have had in our article, we also know that we have not been able to cover everything. For this section, we wanted to take some time to answer other questions that people may have.
The easiest way to convert EER to SEER is by using a our SEER to EER converter to do it for you. Simply enter the required figures and let your computer do the rest. You could try and do it yourself based on instructions we gave earlier, but it is far quicker and more accurate using a converter.
The answer to this depends on where in the country you are. In warmer climates, SEER may give you a more accurate rating. However, if you live in a cooler climate with varying temperatures in different seasons, EER will be much more accurate.
A good EER rating will be as high as possible. Aim for something in the ‘A’ category, between 92 and 100 to know that your appliance is as efficient as it can be. If an ‘A’ rating is not possible, try ‘B’ or ‘C’. Any lower and you risk having an inefficient appliance.
Yes! The higher the EER rating, the more efficient an appliance (in this case, an air conditioning unit) is likely to be. This will conserve more energy and save money over the year.